The output carry is designated as C OUT and the normal output is designated as S. The first two inputs are A and B and the third input is an input carry as C-IN.

Vhdl Code For Full Adder Coding Computer Science Binary Number
The main difference between a half adder and a full adder is that the full-adder has three inputs and two outputs.

. After repeating this step for the rest of the inputs we get the final code is. Each row considering to be a case. For instance considering input 000 A0 B0 Cin0 the output is 00 S0 Cout0 3b000.
9 rows With the above full adder truth-table the implementation of a full adder circuit can be. The operation performed in a binary adder obeys the rules of binary addition. The two inputs are A and B and the third input is a carry input C IN.
Thus full adder has the ability to perform the addition of three bits. Full Adder is the circuit that consists of two EX-OR gates two AND gates and one OR gate. Truth Table.
FULL ADDER TRUTH TABLE VERIFY THE TRUTH TABLE full adder truth tablefull adder truth table and circuit diagramfull adder truth table explanationfull a. Here two bits corresponding to 2 n are added and the resultant is then added to the carry from the 2 n-1 digit. Begin S 0.
A full subtractor FS is a combinational circuit that performs a subtraction between two bits taking. CoutabCinab Full Adder Circuit And Its Construction Truth Table. Truth Table for a Full Adder.
It is used in Multiple bit addition digital processors etc. These are typically referred to as A B and C-IN respectively. Full Adder Truth Table.
Here 0 is logic low and 1 is logic. Full Subtractor Truth table Logic Diagram. The output carry is designated as C-OUT and the normal output is designated as S which is SUM.
It is used for the purpose of adding two single bit numbers with a carry. Full adder circuit theory truth table diagram javatpoint half and with logic working binary definition using a pair of adders digital bcd an overview carry input sum output 2 bit schematic n gates in proteus designing only design 4 ripple 5 parallel subtractor block combinational circuits define draw the its introduction. Full Adder is the adder that adds three inputs and produces two outputs which consist of two EX-OR gates two AND gates and one OR gate.
Half subtractor and full subtractor. The truth table of the Full Adder Circuit is shown below. The two outputs of the full adder are known as sum and carry-out.
A subtractor is a digital logic circuit in electronics that performs the operation of subtraction of two number. Identify the input and output variables-Input variables A B C in either 0 or 1 Output variables S C out where S Sum and C out Carry. Full adder contains 3 inputs and 2 outputs sum and carry as shown-.
The log ical exp ression for Full-adder SumoverlineA overlineB C_inoverlineA B overlineC_inA overlineB overlineC_inA B C_inAoplus Boplus C_in. Logical expression for full adder is. The full adder truth table and K-map implementation are presented below.
What is a 2 bit full adder truth table. The full adder has two outputs S and C. Full Adder is a combinational logic circuit.
A full adder logic is designed in such a manner that can take eight inputs together to create a byte-wide adder and. These are generally denoted by S and C-OUT. For the full adder we just try to write the statements according to the truth table.
Thus full adder has the ability to perform the addition of three bits. Subtractors are classified into two types. There are eight possible combinations of the three inputs of a full adder.
A binary adder is a digital device and needed for digital computations. Full Adder is the adder which adds three inputs and produces two outputs. A B C-IN A B C-IN A B C-IN A B C-IN C-IN A B A B C-IN A B A B C-IN XOR A XOR B 1247.
The first two inputs are A and B and the third input is an input carry as C-IN. Difference Between Sequential And Combination Logic Circuits. Logical Expression for SUM.
Difference Between Half Adder And Full Adder In Tabular Form. Full Adder Part 2Lecture on full adder explaining basic concept truth table and circuit diagramContribute. Full adder contains 3 inputs and 2 outputs sum and carry as shown- Full Adder Designing- Full adder is designed in the following steps- Step-01.
The binary addition rules are stated as follow. The inputs of the full adder are given as input 1 input 2 and carry-in. A full adder logic is designed in such a manner that can take eight inputs together to create a byte-wide adder and cascade the carry bit from one adder to the another.

Binary Decoder Construction Types Applications Simple Words Binary Binary Number

Pin By Computer World On Projects To Try In 2022 Math Projects To Try Hindi
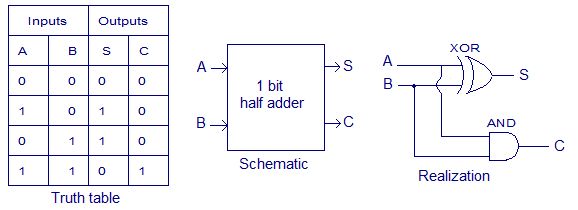
Difference Between Half Adder And Full Adder Coding Informative Truth

3 Bit Multiplier Logic Design Circuit Digital

Carry Save Adder Vhdl Code Coding Carry On Save

Pin By Computer World On Projects To Try In 2022 Math Truth Projects To Try

Binary Multiplier Types Binary Multiplication Calculator Electronic Circuit Projects Electronic Schematics Circuit Projects

Binary Multiplier Types Binary Multiplication Calculator Binary Electronic Schematics Multiplication

Explain Half Adder And Full Adder With Truth Table Goo Gl Y9j0jj Electrical Electronics Binary Number Computer Architecture Binary

Vhdl Code For Full Adder Coding Computer Science Neon Signs

Full Adder Schenatic Electronics Electrical Electronics Circuit Electricity Electrical Components

4 Bit Ripple Carry Adder Vhdl Code Coding Ripple Carry On

Binary Adder Subtractor Construction Types Applications Electronic Engineering Electronic Schematics Binary

Half Adder And Full Adder Circuit Truth Table Logic Diagram Circuit Logic Diagram

Binary Multiplier Types Binary Multiplication Calculator Multiplication What Is Digital Binary

Moore State Machine Vhdl Code Coding States Detector

Half Adder And Full Adder Circuits Using Nand Gates Circuit Circuit Diagram Microsoft

Verilog Code For Pipelined Mips Processor Coding Processor Math


